| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
- python
- netplan
- sudoer
- 패스워드초기화
- NGC
- nvidia-docker
- dmesg
- 리눅스 기본명령어
- 도커
- 도커 설치
- grub
- A100
- 우분투 22.04 패스워드 초기화
- TensorFlow
- V100
- ethtool
- sysstat
- 모니터링
- Cat
- ifconfig
- 엔비디아 도커
- TAIL
- docker
- uname
- nvidia
- Ubuntu 22.04
- passwd
- 우분투
- 우분투패스워드초기화
- CUDA
- Today
- Total
또이리의 Server Engineer
apt-get 과 apt 차이점 본문
apt-get과 apt 차이점
ubuntu apt-get vs apt
오늘 스토리는 우분투에서 apt-get과 apt는 어떻게 다른지 알아보겠습니다.
ATP란 무엇의 약자일까?
Advanced Packaging Tool *.deb 형식의 패키지들을 관리(설치, 삭제, 업데이트)해주는 툴입니다.
우분투 사용하시는 분들은 뭔가 설치하실 때 가장 많이 사용하시는 명령어입니다.
apt vs apt-get
온라인이나 오프라인 패키지 문서를 읽다 보면 어떤 것은 apt-get install을 사용해서 설치하고 어떤 것은 apt install을 사용해서 설치하라고 써져있습니다. 심지어 같은 패키지인데도 서로 다른 경우가 있습니다.
결론부터 말씀드리면 apt-get을 사용하든 apt를 사용하든 큰 차이는 없습니다. 그럼 apt-get과 apt의 차이점은 뭘까요? apt-get을 사용하시든 apt를 사용하시든 내부 동작은 거의 차이가 없습니다.
apt-get는 옵션들이 많아다 보니깐 자주 사용하는 옵션도 있고 그렇지 않은 옵션도 있습니다. 옵션의 사용빈도를 반영하여 apt에서 자주 사용하는 옵션들을 추출해서 사용자들의 편의성을 위해 만들어졌습니다.
그래서 apt가 더 예쁘고 추가적인 정보를 출력해주고 있습니다. 구체적으로 알아보겠습니다.
apt
1. apt를 사용하면 색의 표현도 있고 창 하단에 진행 퍼센티지가 나와서 현재 진행률을 확인하기 편합니다.
2. 출력되는 메시지의 정보가 상세합니다. (apt-get는 추가적으로 옵션을 사용하면 가능합니다. apt는 기본적으로 터미널을 자주 사용하는 사용자에게 배려가 되어있는 느낌입니다.)
일단 한번 보겠습니다.
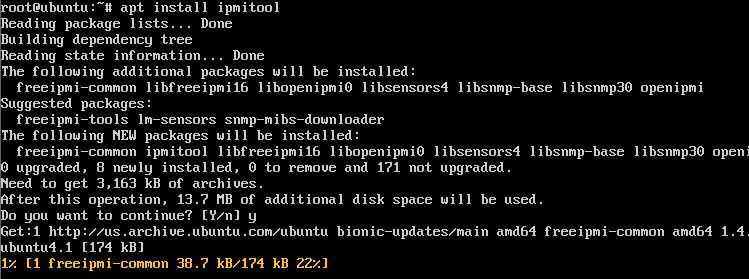

위에 언급했듯이 apt에는 화면 하단에 진행 퍼센티지가 컬러로 표시됩니다. 패키지 설치 시에 저렇게 진행률이 표시되어 보기 편합니다. 반면에 apt-get은 색의 변화도 없으며 각 파일에 대한 진행률은 표시되지만 전체 패키지에 관련된 진행 상태는 표시되지 않습니다.
어떤 걸 사용하는 게 더 좋을까요?
크게 상관은 없습니다. 본인이 사용하기 편하신 걸 사용하면 됩니다. 저는 apt-get이 손에 익숙해져서 주로 사용하지만, 가끔 apt를 사용하면 깔끔하고, 세련됨을 느낍니다.
요즘 우분투를 배우시거나, 접하는 분들은 apt를 많이 사용하시는 걸로 알고 있습니다. apt는 리눅스를 처음 접하거나 특별히 옵션을 사용하는 일이 없다면 사용하시는 걸 권장드립니다.
그러나~! 서버에서 트러블슈팅 해결하시거나 스크립트 작성할 실 때는 apt-get이 더 유용합니다. apt-get은 apt보다 더 많은 세부 옵션들을 가지고 있기 때문에 그만큼 더 많은 기능을 사용할 수 있습니다.
굳이 말하자면 apt-get은 과거부터 오랫동안 사용했기 때문에 당연히 더 안정적이고 호환성이 높기도 합니다. 서버 OS 다루는 사람들이 굳이 뭐 칼라가 더 이쁘고 깔끔해서 무슨 소용이 있겠습니까?라는 생각을 잠깐 해봅니다.
그럼 매뉴얼과 도움말을 한번 체크해보겠습니다.
root@ubuntu:~# apt-get --help
apt 1.6.12 (amd64)
Usage: apt-get [options] command
apt-get [options] install|remove pkg1 [pkg2 ...]
apt-get [options] source pkg1 [pkg2 ...]
apt-get is a command line interface for retrieval of packages
and information about them from authenticated sources and
for installation, upgrade and removal of packages together
with their dependencies.
Most used commands:
update - Retrieve new lists of packages
upgrade - Perform an upgrade
install - Install new packages (pkg is libc6 not libc6.deb)
remove - Remove packages
purge - Remove packages and config files
autoremove - Remove automatically all unused packages
dist-upgrade - Distribution upgrade, see apt-get(8)
dselect-upgrade - Follow dselect selections
build-dep - Configure build-dependencies for source packages
clean - Erase downloaded archive files
autoclean - Erase old downloaded archive files
check - Verify that there are no broken dependencies
source - Download source archives
download - Download the binary package into the current directory
changelog - Download and display the changelog for the given package
See apt-get(8) for more information about the available commands.
Configuration options and syntax is detailed in apt.conf(5).
Information about how to configure sources can be found in sources.list(5).
Package and version choices can be expressed via apt_preferences(5).
Security details are available in apt-secure(8).
This APT has Super Cow Powers.
root@ubuntu:~#
root@ubuntu:~# man apt-get | wc -l
345
root@ubuntu:~# apt --help
apt 1.6.12 (amd64)
Usage: apt [options] command
apt is a commandline package manager and provides commands for
searching and managing as well as querying information about packages.
It provides the same functionality as the specialized APT tools,
like apt-get and apt-cache, but enables options more suitable for
interactive use by default.
Most used commands:
list - list packages based on package names
search - search in package descriptions
show - show package details
install - install packages
remove - remove packages
autoremove - Remove automatically all unused packages
update - update list of available packages
upgrade - upgrade the system by installing/upgrading packages
full-upgrade - upgrade the system by removing/installing/upgrading packages
edit-sources - edit the source information file
See apt(8) for more information about the available commands.
Configuration options and syntax is detailed in apt.conf(5).
Information about how to configure sources can be found in sources.list(5).
Package and version choices can be expressed via apt_preferences(5).
Security details are available in apt-secure(8).
This APT has Super Cow Powers.
root@ubuntu:~# man apt | wc -l
85
root@ubuntu:~#매뉴얼의 라인 수만 보아도 apt는 apt-get의 4분의 1 양 밖에 되지 않습니다..
사용빈도수가 낮은 옵션들이 축소된 것입니다.
위에서 설명드렸듯이 처음 접하시거나 옵션 사용이 적으신 분들은 apt를 사용하시는 게 권장됩니다.
숙련자나 전문적으로 사용하시는 분들 옵션 사용이 많으신 분들은 말씀 안 드려도 알아서 사용하시리라 생각됩니다.
'Linux Engineer' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 루트 권한 부여하기 리눅스 - root permission (0) | 2020.11.22 |
|---|---|
| sudo 권한 부여하기, 리눅스 su su - 차이 (0) | 2020.11.21 |
| 리눅스 top 명령어 (0) | 2020.11.19 |
| netplan bonding 우분투 본딩 (0) | 2020.11.18 |
| 우분투 멀티 IP - 다중 IP 설정 (0) | 2020.11.17 |




